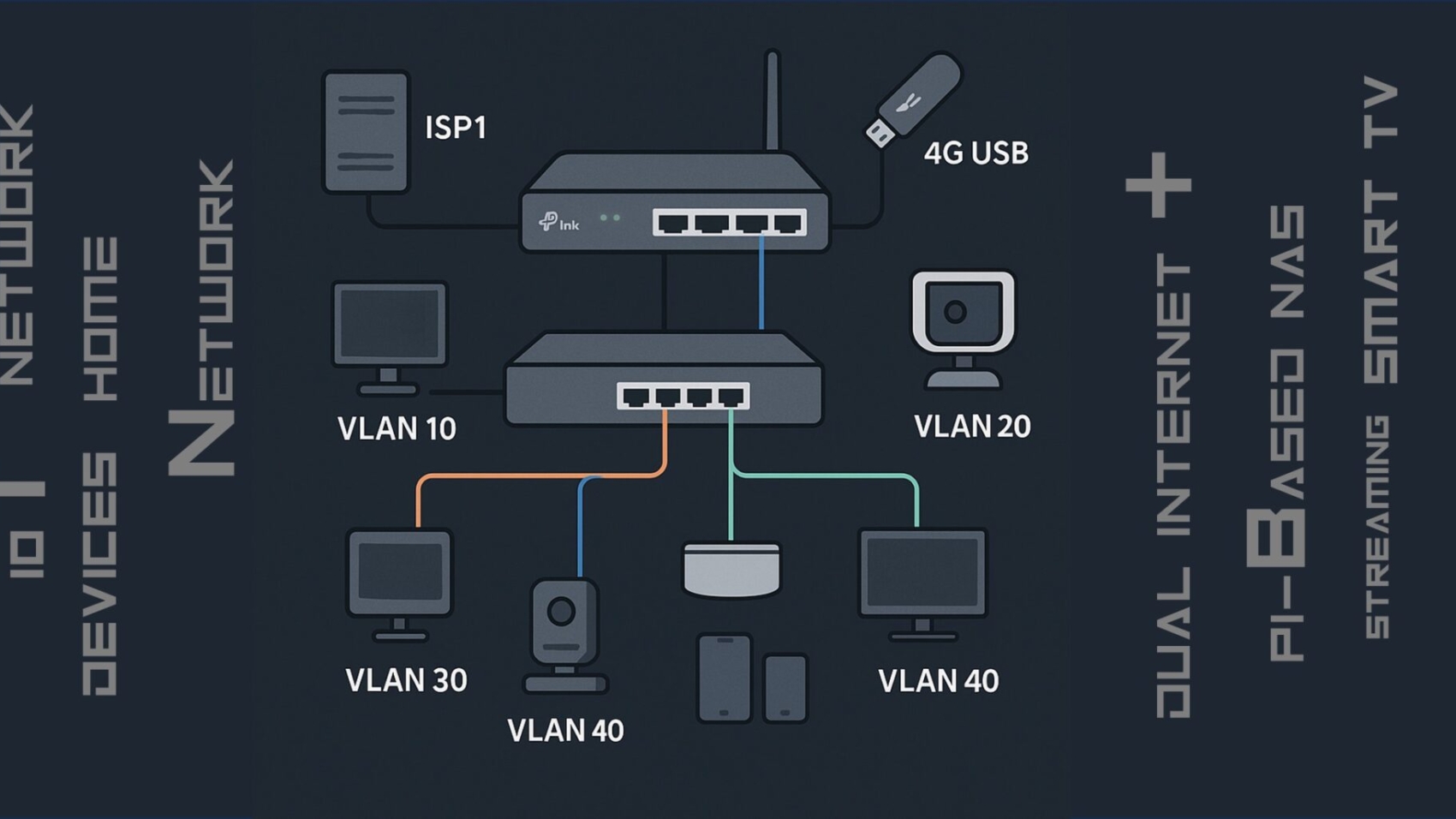
In today’s connected homes and SMB setups in India, where you juggle CCTV, IoT appliances, work PCs, and dual-ISP routers, a managed Router isn’t just a convenience—it’s becoming a necessity.
So, What Makes a Managed Router Special?
1. VLANs & Trunking—Security Made Simple
Managed Router let you create distinct virtual networks. Whether it’s keeping CCTV isolated, buffering IoT traffic, or segmenting guest Wi-Fi, VLANs let you do this without buying extra hardware—keeping your home secure and organized .
2. Smart Traffic Management (QoS, IGMP, Throttling)
Let’s be honest—nothing’s more frustrating than your Zoom call freezing just when you’re trying to talk to a client or team lead. Meanwhile, someone in the next room has fired up a 4K YouTube stream, hogging all the bandwidth. That’s where smart Router’s earn their keep.
With a managed Router, you can tell your network:
“Work-from-home traffic first. Entertainment can wait.”
Features like QoS (Quality of Service) allow you to prioritize your important devices—like your office laptop or VoIP phone—so they get the cleanest, fastest data path.
And if you’ve got 3–4 IP cameras running 24×7? Managed Router with IGMP snooping help keep those streams from overwhelming the network. It ensures video packets only go where they’re needed, not everywhere.
So instead of playing traffic cop manually, let your Router do it.
3. Loop Prevention & Spanning Tree
Messing up cable connections can bring down your entire network. With protocols like Spanning Tree, managed Router’s prevent broadcast storms—even when cables are unplugged and re-plugged randomly .
4. Remote Monitoring & Diagnostics
CLI, SNMP stats, port mirroring—even port-level PoE status—managed Router’s make it easy to keep an eye on your network remotely. That’s enterprise-grade visibility now available at home.
5. Scalable for the Future
Smart features like link aggregation and stacking let you scale from 8 ports to 48+ ports—without buying new gear. You pay for flexibility, not more hardware .
Download Cisco Router Configuration Template
Real-Life Use Case: Dual-ISP, Smart Home Setup
One Mumbai-based professional shared this:
“We had jittery Zoom calls when CCTV streamed 1080p nonstop. After plugging in a managed Router we isolated cameras in VLAN 30, prioritized our work devices in VLAN 10, and set up guest Wi-Fi on VLAN 40. The zoom stability improved instantly.”
Now, 4 IP cameras, 1 running automation, smart plugs, and dual broadband coexist peacefully.
Managed vs. Unmanaged—When Simplicity Wins
Unmanaged Router’s are zero-effort—just plug and play. They’re fine for basic home use or one-off projects. But:
- No VLANs
- No traffic control
- No loop prevention
- No remote diagnostics
As one homelab professional said:
“Once you go managed, you won’t go back.”
When You Definitely Need One
- Multiple device types (IoT, CCTV, guest users, workstations)
- Momentary network reliability is critical (Zoom, VoIP)
- Increasing device count (5+ wired devices)
- Dual-ISP/failover setup
- Remote troubleshooting/access required
Is It Worth the Cost?
Here’s the real-world view:
Yes, managed Router’s cost more than basic ones. But if your home network is starting to resemble a mini data center—with work gear, smart gadgets, and security cameras—it pays off in more ways than one.
You save on:
- 🔄 Time – No more wild goose chases when the Wi-Fi lags
- 🚀 Performance – Smooth bandwidth allocation means fewer bottlenecks
- 🔐 Security – VLANs help separate critical devices from general ones
Think of it like this:
Would you rather install multiple old-school coolers, or invest once in a proper AC system with zoning control?
A managed Router gives you that centralized control and peace of mind, especially if you’re scaling your tech at home or running a hybrid office setup.
For Indian techies balancing home automation, remote work, network security, and multiple ISPs, a managed Router is the foundation of a smart, scalable network. It brings enterprise-level tools into home environments—without the complexity.