Why Router Provisioning Still Wastes Your Time
If you’re an Indian network engineer or ISP field tech, you’ve probably spent hours manually configuring routers—copy pasting commands into terminals, checking logs, and debugging silly typos. Sounds familiar?
This is where automation scripts for router provisioning come into play. These are simple scripts shell, Python, Ansible, or even Expect that configure routers in seconds, without the drama.
Whether you’re deploying 50 TP-Link routers in a society broadband project or rolling out enterprise routers at a campus in Bangalore, automation saves your day.
What Exactly Is Router Provisioning?
In simple words, router provisioning is the process of setting up a new router with all the correct settings:
- WAN/LAN IP configuration
- DNS settings
- Enabling DHCP or Static routes
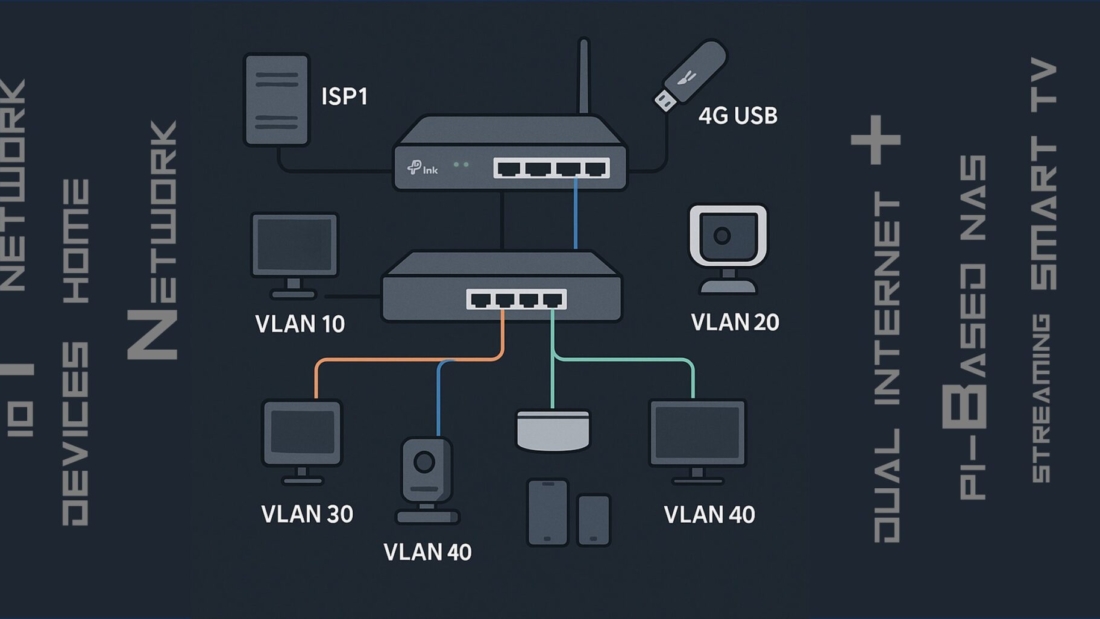
- VLAN tagging
- Pushing firmware updates
- Assigning credentials and SNMP traps
Done manually, this takes time and is error-prone. Automated provisioning means you write the script once and reuse it forever.
Tools You Can Use for Router Automation
If you think automation needs high end gear or expensive platforms, think again. Here’s what works well in Indian setups:
| Tool | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Bash Scripts | CLI automation on OpenWRT/Linux routers |
| Ansible | Bulk provisioning for enterprise routers |
| Python + Netmiko/NAPALM | API based config push on Cisco/Juniper |
| Expect | Automate telnet/SSH interactive sessions |

Most local ISPs, system integrators, and college networks can easily start with Bash or Expect.
Example Script 1: Basic Router Provisioning
#!/usr/bin/expect -f
spawn ssh admin@192.168.0.1
expect "password:"
send "admin123\r"
expect "#"
send "configure terminal\r"
send "hostname TP-Router\r"
send "exit\r"
send "exit\r"
#!/bin/bash // ***** Expect Script for Router Login Automation *****
echo "Provisioning TP-Link Router..."
ssh admin@192.168.0.1 <<EOF
uci set network.lan.ipaddr='192.168.1.1'
uci set network.lan.netmask='255.255.255.0'
uci commit
/etc/init.d/network restart
EOF
echo "Provisioning complete."
Why Techies Are Using This More?
- No need to touch 100 routers individually
- Reduces technician training cost
- Cuts down setup time from 30 minutes to 3
- Saves you from accidental misconfiguration
With the explosion of broadband demand in Indian towns, WISPs and system integrators are waking up to the power of scripting.
Stop Doing It Manually
You’re not working in 2010. It’s 2025 and the networks you manage deserve better. With a few reusable automation scripts for router provisioning, you can eliminate hours of grunt work and avoid silly mistakes that cause huge outages.
Want a jumpstart? We’re building a free GitHub repo with ready-to-use provisioning scripts for Indian routers (TP-Link, D-Link, Netgear, MikroTik, and more). Stay tuned at TechieBano.com.