In today’s rapidly scaling enterprise and data center networks, choosing the right fiber transceiver is critical. Among the most common types are LR (Long Range) and SR (Short Range) SFPs. This guide breaks down the 5 key differences between LR and SR SFPs to help network engineers and IT professionals make informed decisions.
1. Transmission Distance
- SR SFP (Short Range): Typically supports up to 300 meters using OM3 multimode fiber.
- LR SFP (Long Range): Designed for distances up to 10 kilometers over single-mode fiber (SMF).
SR modules are perfect for in-building links, while LR SFPs are ideal for building-to-building or WAN uplinks.
2. Wavelength
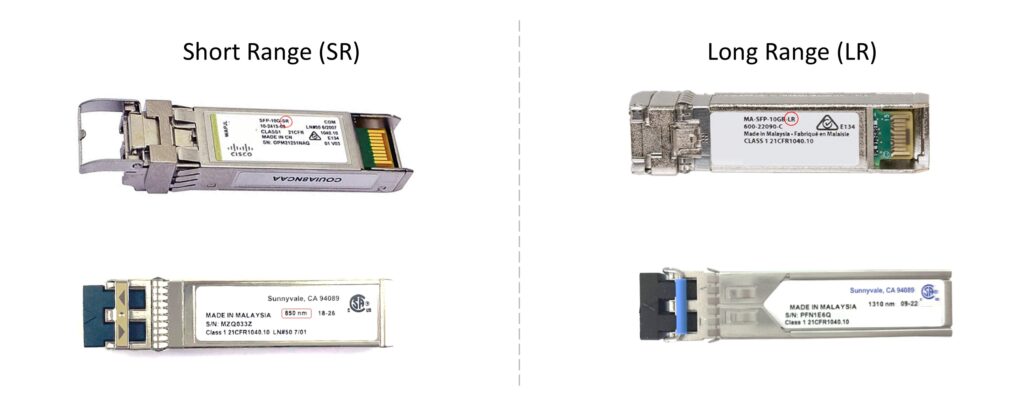
- SR SFP: Operates at 850 nm wavelength.
- LR SFP: Operates at 1310 nm wavelength.
These wavelength differences affect how data is transmitted across the fiber type and distance.
3. Fiber Type Compatibility
- SR SFPs: Work with Multimode Fiber (MMF), usually OM2, OM3, or OM4.
- LR SFPs: Require Single-Mode Fiber (SMF).
Tip: Use color-coded cables (orange/aqua for MMF, yellow for SMF) to visually track fiber types.
4. Use Case Scenarios
- SR SFP: Common in data centers, server racks, and short-distance campus networks.
- LR SFP: Used in enterprise backbones, metro Ethernet, and data center interconnects.
5. How to Identify LR vs SR SFPs
Physically or via CLI:
- Check the label for terms like “SR”, “SX”, or 850 nm” (SR), and “LR”, “LX”, or 1310 nm” (LR).
- On Cisco, Juniper, or MikroTik devices, use commands like
show interfaces transceiverordisplay transceiver.
show interfaces transceiver
display transceiver
Vendor Clues:
- Some vendors color-code pull-tabs: blue/beige for SR, yellow for LR.
Real-World Example:
A data center administrator setting up a spine-leaf architecture may deploy SR SFPs between top-of-rack switches and LR SFPs from aggregation switches to a data center interconnect (DCI).
LR (Long Range) and SR (Short Range) are optical transceivers used for different distances and fiber types in a network.
LR SFP is ideal for long distances, supporting up to 10 km on single-mode fiber.
No, SR SFPs are designed specifically for multimode fiber.
They’re used in data centers and short-distance intra-building connections.


